Ethereum Validator Queue
There are two main factors that determine the Ethereum validator entry queue and node activation times:
- Demand balance
- Protocol-imposed time limits for security reasons can be said.
First, regarding demand balance, institutional investors are shifting capital to staking in order to increase value while holding their investments through the proof-of-stake algorithm-based network system, as their market share in the crypto industry grows. At this point, as the flow of ETH wanting to become validators increases, it begins to push the system’s demand balance limits. Since this is a factor on which the activation time of nodes depends, it directly extends the average activation time.
The second factor, the limitation imposed for protocol security, requires restricting the input-output changes of the proof-of-stake algorithm. This means that only a limited number of validators are activated per epoch, and only a limited number of validators can exit. Currently, applications are accumulating because demand exceeds the limit, and consequently, a queue forms and grows. This growing queue directly affects the activation time. The importance of this mechanism in terms of security is actually to keep the network’s balance and security close to optimal by controlling sudden increases and decreases in the validator set.
Another important piece of data that has changed since 2025 is that there is almost no validator waiting to exit. In this case, the increasing high demand means that there is no room to exit because no one is leaving, and the queue is getting longer. This also extends the dynamic activation time. It is estimated that the instantaneous activation time can be up to 45 days.
This is roughly due to a surge in demand and the fact that internal players are not exiting and are forming a demand queue to enter. So why has such a surge in demand occurred?
In Ethereum, price expectations are well above the current price, and the attractive financial contribution of the staking algorithm and the increasing popularity of liquid staking tokens are driving stake demand. This also lengthens the entry queue because everyone who sees a “staking opportunity” joins the queue. This raises the question: will this have an impact on Ethereum prices?
What is the Impact on Pricing?
As the validator queue grows, a very significant amount of ETH is actively locked (demand for staking is increasing). This reduces the amount of “sellable” ETH in circulation and creates a squeeze on the supply side, which normally puts upward pressure on prices.
So, how did pricing behave in previous periods based on this data? How effective an indicator is it really? Let’s ask these questions and examine them.
Looking at the on-chain side.
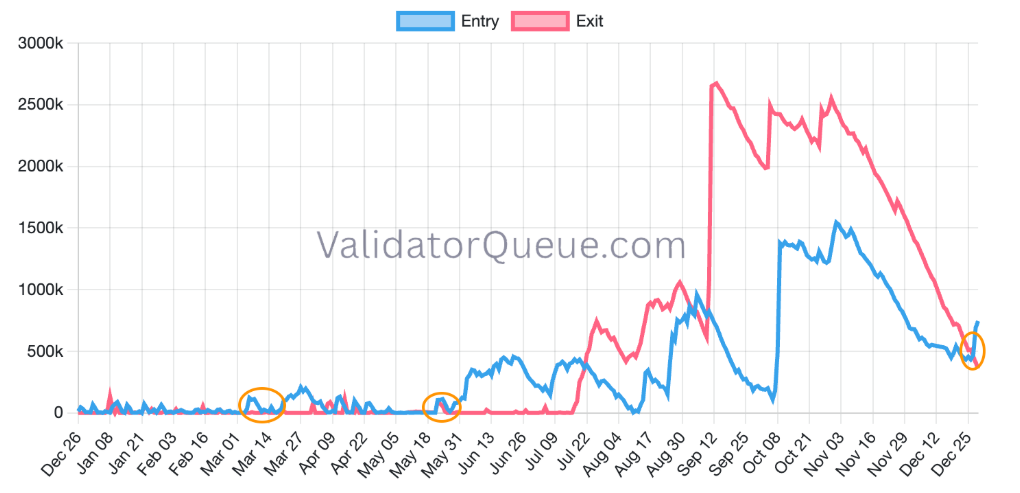
Last year, in mid-March, Ethereum experienced a local dip to around $1,500 as validator inflows exceeded validator outflows. This was followed by a near-unstoppable rally that pushed prices up to nearly $2,500. Ethereum lingered in this range for about two months before surging to $4,955 in July, driven by a massive increase in entries around mid-May. In September, withdrawal requests from staking began to exceed entry requests, leading to a sharp transition. Looking at the price chart, exit requests from $4,955 appear in red, similar to the validator demand chart, accompanied by sharp price candles.
The only conclusion we can draw from this is that the ratio of those wanting to enter for validation to those wanting to exit actually gives us an important preliminary idea about the potential buying and selling direction. Considering that the ratios in the current time frame are entry-heavy, we can say that the data we have examined is definitely meaningful and that as long as it continues this way, it creates an ideal environment for Ethereum’s price rise.





