What Does the CLARITY Act Aim to Achieve?
The lack of clarity regarding the legal status of digital assets in the US created significant uncertainty for both investors and companies. In this context, the lack of regulation regarding crypto markets remained on the US Congress’ agenda for a long time. To eliminate this uncertainty, a bill called the Digital Asset Market Clarity Act of 2025 (CLARITY Act) was drafted and brought to the agenda in the House of Representatives. This bill aimed to create a more understandable legal framework for crypto assets. The bill sought to establish a clearer distinction between which crypto assets would be considered securities and which would be considered commodities. This aimed to establish a clearer basis for the long-debated division of authority between the SEC and the CFTC.
According to the bill, most crypto assets were to be classified as digital commodities and left under the supervision of the CFTC. In contrast, the initial sale of crypto assets was planned to be subject to securities legislation. This made the rules governing the activities of crypto companies and exchanges clearer. The CLARITY Act was not limited to classification alone. It also imposed additional obligations on crypto exchanges, such as keeping customer assets separate from their own accounts, disclosing potential conflicts of interest to the public, and strengthening risk management processes. These regulations aimed to reduce market uncertainty, increase consumer protection, and create a more transparent market structure.
However, some provisions in the draft text sparked serious debates within the industry. Major market players, notably Galaxy Digital and Coinbase, argued that the regulation was overly stringent and mounted such strong opposition that it led to the postponement of the vote in the Senate Banking Committee. In this report, we will examine the potential impact of the CLARITY Act on users and institutions, based on these objections.
Galaxy Digital & Coinbase’s Objections
Galaxy Digital and Coinbase argued that certain provisions of the CLARITY Act draft would constitute direct intervention in market operations rather than providing regulatory clarity. They therefore explicitly opposed the text. The objections raised by both institutions pointed to the potential operational and competitive consequences of the regulation.
The table below summarizes Galaxy Digital and Coinbase‘s key criticisms of the bill and the potential market impacts in a comparative manner:
| CLARITY Act Content | Galaxy Digital’s Objection | Coinbase’s Objection | Potential Market Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Intervention Authority | Regulatory agencies are granted excessively broad and ill-defined powers. | These powers are not tied to objective criteria and are open to arbitrary application. | Legal uncertainty increases, investment appetite decreases. |
| Classification of Crypto Assets | Concerns that many crypto assets may effectively fall under the scope of securities. | Risk of retroactive sanctions. | Listings decrease, the market shrinks. |
| Crypto Funds | Fund managers’ operational flexibility is significantly reduced. | Regulatory costs are becoming unpredictable. | Institutional capital outflow. |
| Innovation Risk | US leadership in crypto innovation could be undermined. | Entry barriers for start-ups are increasing. | Decline in the number of new projects. |
| Compliance Burden | Unsustainable costs are arising for small and medium-sized funds. | Reporting burden on exchanges is disproportionate. | Consolidation leads to the elimination of smaller players. |
| International Competition | US-based companies are at a disadvantage. | EU and Asian markets are becoming more attractive. | Companies relocating abroad. |
| User Impact | Product and fund diversity may decrease. | US users may have limited access to certain services. | Decrease in liquidity and trading volume. |
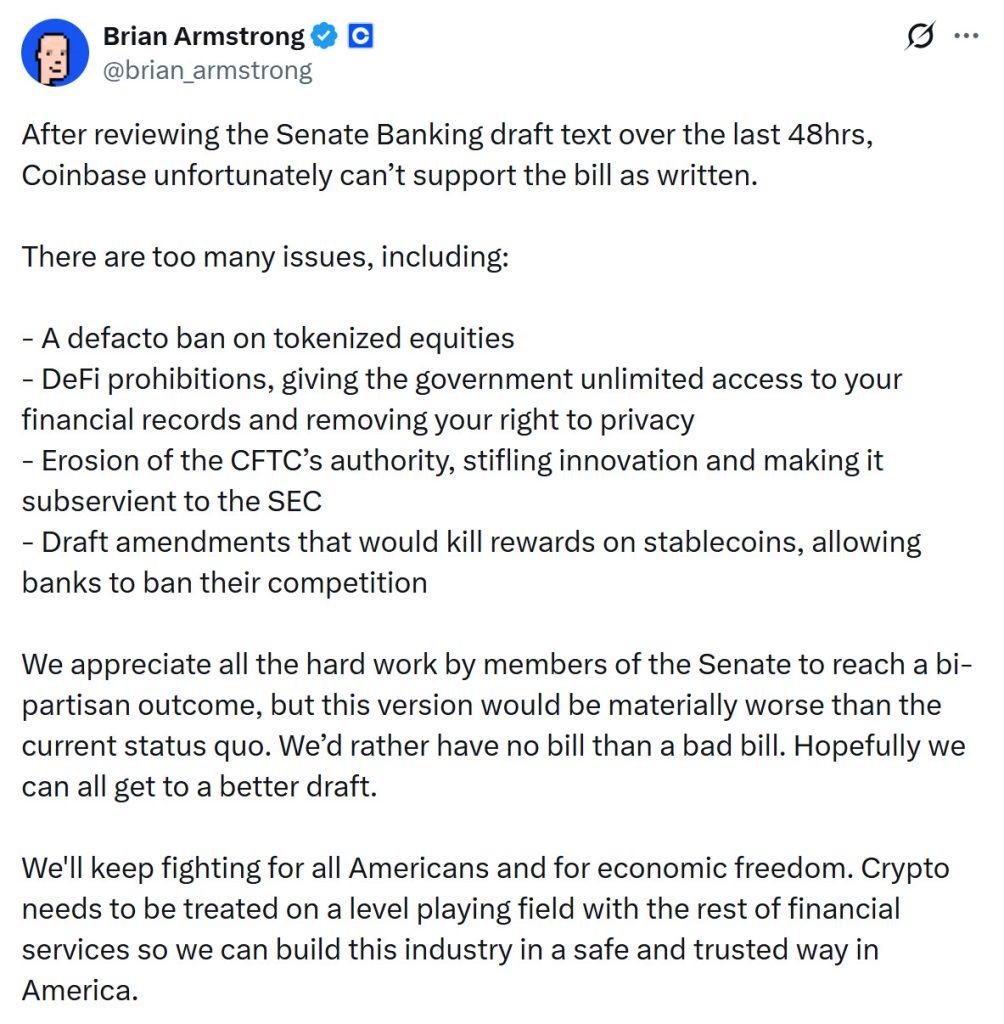
In addition to Galaxy Digital’s criticism at the corporate level, Coinbase’s top management also expressed their opposition. Coinbase CEO Brian Armstrong stated on his official X account that the latest draft prepared by the Senate Banking Committee could not be supported in its current form.
Source: Brian Armstrong X Account – https://x.com/brian_armstrong
Armstrong stated that the bill effectively bans tokenized stocks, restricts decentralized finance (DeFi) activities, and eliminates reward mechanisms provided through stablecoin balances, giving banks a competitive advantage. He also emphasized that the regulation would weaken the CFTC’s authority and create a structure that largely leaves the crypto market under SEC oversight. For these reasons, Armstrong stated that the current draft could lead to even more negative outcomes than the current uncertain legal environment.
Potential Impacts for Users
The CLARITY Act’s fundamental promise for users is a reduction in legal uncertainty through the clarification of crypto asset classifications. However, certain provisions in the draft could have restrictive consequences for individual investors.
Key risks include:
- The removal of interest and reward models offered on stablecoin balances,
- A decrease in product diversity due to crypto assets being classified as securities,
- Weakening of financial privacy due to increased regulatory oversight,
- Erosion of investor confidence due to the possibility of retroactive penalties.
In this respect, although the bill aims to protect investors, it has the potential to create a restrictive effect in terms of market depth and options.
Potential Impacts for Institutions
For institutions, the CLARITY Act has the potential to provide legal clarity and legitimacy on the one hand, but on the other hand, it imposes significant operational burdens. Galaxy Digital argues that increased oversight of fund management will reduce operational flexibility and weaken investor interest. Coinbase states that the uncertainty surrounding token listing processes and the prohibition of stablecoin reward models will directly negatively impact their business models.
Furthermore, the bill in its current form could push the US into a stricter regulatory environment on a global scale, directing companies towards markets with more flexible regimes, such as Europe and Asia. This situation carries the risk of reducing the US’s weight in crypto innovation in the long term.
Conclusion
The CLARITY Act is one of the most comprehensive efforts to date to regulate the crypto asset market in the US and has the potential to provide legal clarity. However, Galaxy Digital and Coinbase argue that the bill grants regulatory agencies overly broad intervention powers and effectively bans stablecoin rewards and tokenized securities. These objections led to the postponement of the Senate vote.
In summary, the outcome of the CLARITY Act appears to depend on striking a balance between protecting investors and the need to facilitate innovative crypto projects. In its current form, the bill faces serious criticism that some of its oversight powers are overly broad. Therefore, revising the text to address the fundamental concerns raised by the industry is crucial for both the sustainable growth of the crypto market and the preservation of the US’s global position in this field.
Disclaimer
This content is for informational and educational purposes only; it does not constitute legal advice, regulatory guidance, or investment advice.
The assessments contained herein regarding the Digital Asset Market Clarity Act (CLARITY Act), the classification of digital assets, SEC–CFTC jurisdiction sharing, and the views of institutions such as Galaxy Digital and Coinbase are based on publicly available information, reports, and analyses at the time of writing. Legislative processes are subject to political deliberation, changes, and regulatory revisions. Therefore, the final scope of regulation, methodology, or legal interpretations may differ materially from those stated herein.
Statements regarding potential impacts on users, institutions, market structure, innovation environment, or product access are analytical assessments; they do not constitute definitive conclusions or warranties. Regulatory changes can affect crypto asset markets in unpredictable ways, and the legal framework may vary from country to country.
None of the information contained in this content should be construed as advice to buy, sell, hold, or use any digital asset, platform, or financial product. Readers are advised to conduct their own research (DYOR) and seek professional advice from qualified legal, financial, or regulatory experts where necessary.
The author and publisher cannot be held liable for any direct or indirect damages arising from the use of this content.